Confirmation
qSOFA, SIRS & Sepsis Criteria
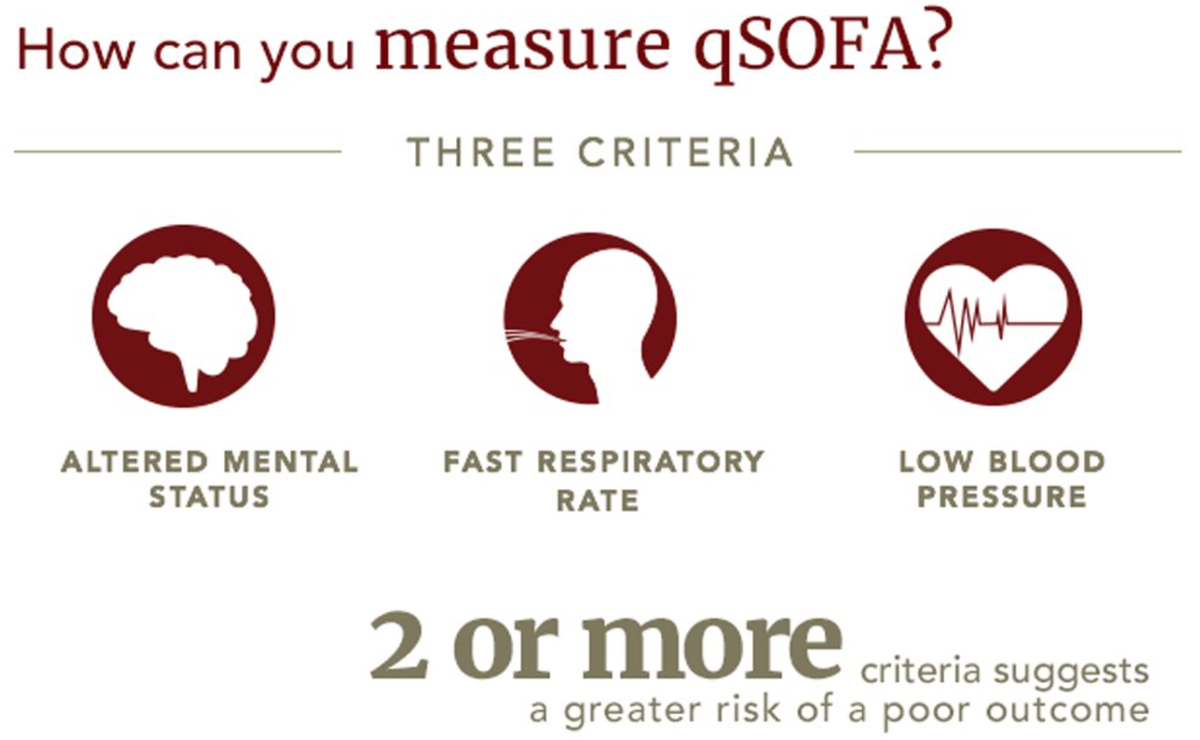
qSOFA
The Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (qSOFA) screening tool is recommended to determine risk stratification of septic patients
SIRS
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) is a more sensitive screening tool for early detection of septic patients. It has more false positives (ie, non-septic patients who fit the criteria), but is more likely to detect patients before they develop qSOFA.
SIRS Criteria
SIRS (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) is defined as two or more of the following that are new to the patient.
- Hyperthermia >38.3°C or Hypothermia <36°C
- Acutely Altered Mental Status
- Tachycardia >90 bpm
- Tachypnea >20 bpm
- Hyperglycemia (6.7mmol/L) in the absence of diabetes
- Leukocytosis (>12,000 μL-1) or Leukopenia (<4,000 μL-1)
Sepsis Criteria
Two or more SIRS signs that are new to the patient
PLUS suspicion or diagnosis of new infection
Severe Sepsis
Sepsis PLUS one or more of the following (signs of organ dysfunction, hypotension or hypo-perfusion)
- Hypotension (<90/60 or MAP <65)
- Lactate >2
- Areas of mottled skin or capillary refill >3 seconds
- Creatinine >2.0 mg/dl
- Platelet count <100,000
- Acute renal failure or urine output <0.5 ml/kg/hr for at least 2 hours
- Cardiac dysfunction
- Acute lung injury or ARDS
Pediatric Age-Specific SIRS Criteria
|
Age |
HR (high) |
HR (low) |
Resp Rate |
Min Systolic |
|
Birth – 1wk |
>180 |
<100 |
>60 |
60 |
|
1wk – 1mo |
>180 |
<100 |
>50 |
75 |
|
1mo – 2yrs |
>180 |
<90 |
>35 |
75 |
|
2 – 5yrs |
>140 |
N/A |
>30 |
75 |
|
6 – 12yrs |
>130 |
N/A |
>20 |
83 |
|
>12yrs |
>110 |
N/A |
>20 |
90 |
Severe Pediatric Sepsis
Includes SIRS and two or more of the following signs of hypo-perfusion or organ dysfunction that is new and not explained by other known etiology of organ dysfunction:
- Proven need for >50% FiO2 to maintain saturation ≥ 92%
- Need for nonelective invasive or noninvasive mechanical ventilation
- Glasgow Coma Score ≤11
- Acute change in mental status with a decrease in Glasgow Coma Score ≥3 points from abnormal baseline
In Hospital Criteria
- Unexplained metabolic acidosis: base deficit > 5.0 mEg/L
- Increased arterial lactate > times upper limit of normal
- Oliguric: urine output <0.5 mL/kg\hr
- Core to peripheral temperature gap > 3°C
- PAO2/FIO2 <300 in absence of cyanotic heart disease or preexisting lung disease
- PaCO2 >65 torr or 20 mm Hg over baseline PaCO2
References:
Dellinger, R. Phillip et al, Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2012. Critical Care Medicine, Feb.2013, Vol.41, No 2.