Confirmation
PR51: Prehospital Fibrinolysis
Applicable To
Introduction
This procedure has been developed to support out-of-hospital reperfusion in patients experiencing ST elevation myocardial infarctions (STEMI) in areas without immediate access to cardiac catheterization laboratories. It requires specific training in out-of-hospital reperfusion. This procedure is not a substitute for sound clinical judgment and collaborative decision-making.
Indications
ST elevation myocardial infarction in an area > 60 minutes drive time to primary percutaneous coronary intervention facilities.
Contraindications
Extensive contraindications: see procedure for complete details.
< 60 minute drive time to PPCI
Procedure
All patients:
- Apply defibrillator pads
- Provide supplemental oxygen if SpO2 is less than 90%
- Acquire and interpret 12 lead ECG -- transmit to CliniCall/EPOS immediately if STEMI markers present
- Continue to obtain serial 12 lead ECGs every 15-30 minutes during care and conveyance
- Establish IV access (two large-bore lines recommended), including saline lock
- Avoid right hand/wrist where possible; attempt to keep IVs on same limb where practicable
- Obtain baseline history and examination (details below)
- Acetylsalicylic acid 160 mg PO chew and swallow
- Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg spray every 5 minutes x 3 doses for ongoing chest pain if systolic blood pressure is greater than 90 mmHg
- FentaNYL 25-50 mcg IV every 5 minutes as required (maximum 300 mcg) or MORPHine 2.5 mg IV every 5 minutes as required (maximum 15 mg) if systolic blood pressure is greater than 90 mmHg for severe, refractory chest pain
- DimenhyDRINATE 25-50 mg IV every 4 hours as required for nausea
- Atropine 0.6 mg IV/IM every 5 minutes as required (maximum 3 mg) for symptomatic bradycardia
- Contact CliniCall / EPOS after appropriate history, physical, inclusion / exclusion criteria reviewed with patient and ECG sent
History (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Chest pain
- Crushing, burning or dull retrosternal
- Radiating to _________
- Worse with activity or exertion
- Worse while supine, improves while sitting forward
- Sharp (knife- or needle-like) and worse with respiration
- Sharp stabbing or tearing
- Focal neurological symptoms (limb weakness, visual change, speech difficulties)
- Loss of consciousness associated with presentation
- Associated symptoms (nausea, diaphoresis, SOB)
- Comorbidities (HTN, diabetes, smoking, familial hx)
Physical examination (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Pupils are equal in size, round, and reactive to light
- GCS __/15, HR ___, RR ___, Sp02 ___%
- Blood pressure
- Right arm
- Left arm
- Systolic difference is > 20 mmHg?
- Pulses present and equal in left and right arms
- Pulses present and equal in both carotid arteries (caution: check one at a time)
- Air entry is equal to both lung bases
- Crepitations heard in lung fields?
- Murmur heard on cardiac auscultation
- Moves all four limbs against resistance.
Indications for primary percutaneous coronary intervention (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Contraindication to tenecteplase, OR
- Cardiogenic shock, OR
- Severe acute heart failure, OR
- Recurrent VF/VT, OR
- First medical contact to balloon time < 120 minutes (<60 minute drive time) OR
- Diagnosis of STEMI in doubt
Indications for tenecteplase (TNK) administration (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Time from onset of chest pain is less than 12 hours
- Chest pain is consistent with myocardial ischemia
- ECG changes are consistent with STEMI:
- In men, new STE at J point ≥ 2.0 mm (0.2 mV) in V2 and V3
- In women, new STE at J point ≥ 1.5 mm (0.15 mV) in V2 and V3
- New STE at J point ≥ 1.0 mm (0.1 mV) in other contiguous leads
- New ST depression at the J point ≥ 1.0 mm (0.1 mV) in leads V1/V2 and STE ≥ 1 mm (0.1 mV) in posterior leads V7-V9
Absolute contraindications for tenecteplase (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Any prior bleeding in the brain
- Structural abnormality of arteries or veins in brain
- Known tumour in brain
- Ischemic stroke within the last 3 months
- Significant closed head or facial trauma in the last 3 months
- Brain or spinal injury within the last 2 months
- Active bleeding or bleeding susceptibility (excluding menses)
- Severe uncontrolled hypertension (unresponsive to emergency therapy)
- Suspected aortic dissection
Relative contraindications for tenecteplase (check all that apply, and review with EPOS):
- Known intracranial pathology not covered by absolute contraindications
- Dementia
- Prior stroke greater than 3 months ago
- Major surgery in the past 3 weeks
- Internal bleeding in the past 4 weeks
- Blood pressure greater than 180 systolic, or 110 diastolic on presentation
- History of chronic, severe, poorly controlled hypertension
- Traumatic or prolonged (> 10 minutes) chest compression/CPR
- Pregnancy
- Active stomach ulcers
- Currently taking blood thinners (i.e., warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants)
- Non-compressible vascular punctures
Tenecteplase criteria -- must satisfy all -- check when complete:
- NO indications for primary PCI
- Case discussed and ECG reviewed with EPOS
- NO absolute contraindications
- Relative contraindications, if any, reviewed with EPOS
- Risks, benefits, and alternatives to tenecteplase have been reviewed with patient, and CONSENT (verbal) to treatment with TNK is obtained
Tenecteplase action (choose one):
- DOES NOT MEET TNK criteria
- Action: provide usual care and transport
- DOES MEET TNK criteria
- Action: administer TNK as per protocol
Tenecteplase informed consent script (read to patient):
"You are having a heart attack and would benefit from potentially life-saving clot dissolving medications. When given early, these drugs can prevent the heart attack from progressing and causing further heart muscle damage. They can even prevent death from a heart attack and related complications. There are some serious risks associated with the use of these medications, though, that you need to be aware of. Those risks include, but are not limited to, bleeding, strokes, and heart rhythm problems. The risk of bleeding in the brain is less than 2-3%. We are able to deliver these therapies to you immediately, and the sooner you get these medications the sooner blood supply may be restored to your heart. You have the option of declining these medications and waiting to be assessed when you go to the hospital, although it is important to know that if treatment is given more than 12 hours after onset of symptoms, treatment may cause more harm than benefit. Do you give consent to receive this treatment?"
Tenecteplase Protocol (check when complete)
| 75 years of age or less | over 75 years of age |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
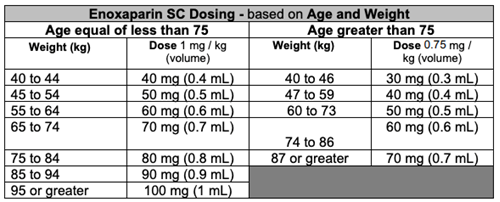
NB: In certain situations, the consulting physician may recommend the administration of enoxaparin and clopidogrel without tenecteplase.
Tenecteplase dosing based on age and weight
| Weight (kg) | TNK dose (mg) in patients < 75 years | TNK dose (mh) in patients > 75 years |
| < 60 | 30 mg (6 mL) | 15 mg (3 mL) |
| 60 to < 70 | 35 mg (7 mL) | 17.5 mg (3.5 mL) |
| 70 to < 80 | 40 mg (8 mL) | 20 mg (4 mL) |
| 80 to < 90 | 45 mg (9 mL) | 22.5 mg (4.5 mL) |
| ≥ 90 | 50 mg (10 mL) | 25 mg (5 mL) |
Post tenecteplase administration:
- Notify receiving ER physician of patient arrival, and report:
- Patient started on TNK as per physician orders
- TNK administered at _____, with patient weight and dosage
- Any protocol medications not administered and rationale
- Current patient status (GCS, appearance, vital signs, chest pain, etc.)
- Estimated time of arrival in emergency department
- Where possible: PHN, name, date of birth for pre-arrival registration
- After TNK administration, monitor neurological vitals every 15 minutes for the first hour, and then every 30 minutes thereafter
- After TNK administration, repeat ECG every 15-30 minutes and at 60 minutes. Notify EPOS if:
- Ongoing chest pain
- Ongoing ST elevation (less than 50% resolution)
- Hemodynamic instability develops
- Transport to closest emergency department:
- Complete all relevant sections of ePCR, including ACP prehospital fibrinolysis form (Other Assessments), Hospital Consultation (Procedures), patient weight, vital signs
- Attach 12 lead ECG to ePCR
- Handover report is critical to avoid repeat medication administration. Ensure that receiving staff are informed.
- Send e-mail including the event number to clinicalpractice@bcehs.ca
Notes
Tenecteplase kit Build Instructions for ACP’s (appendix 2)
- Juice box or water bottle
- Clopidogrel 75mg tablet (in strip packaging) in labelled zip lock bag
- Clopidogrel 300mg tablet (in blister) in labelled zip lock bag
- Enoxaparin 30mg syringe + IV adapter + IV flush syringe + alcohol swab in zip lock bag
- Enoxaparin 100mg syringe + alcohol swab in zip lock bag
- TNK 50mg kit + alcohol swab + IV flush syringe add flush and swab into TNK box
- Put expiry sticker (provided by pharmacy) on outside of kit
- Paramedic partner to double check
- Seal kit with plastic security zip-tie
Tenecteplase kit removal from Omnicell-Interior ACP’s ONLY
- Paramedic to sign into main ER Omnicell using credentials
- Remove Tenecteplase kit under name of current STEMI patient a. Item Name: BCEHS use only Tenecteplase
- Prepare kit according to “Tenecteplase kit build instructions for paramedics” (see appendix 2)
- Label outside of kit with expiry label
- Second paramedic to perform double check of kit, and seal with security zip-tie
- One prepared kit to be stored on each ACP car at all times
- If kit expires before use, return all medications to the pharmacy return bin in ED med room and remove a new kit under the generic patient *BCEHS Use Only TNK Kit* found on the Local Patient List
- Medications must be stored between 2-30◦C. If car temperature goes above 30◦C please transfer kits to the station and contact hospital pharmacy department for further instructions
Resources
Drug monographs:
- Acetylsalicylic acid
- Nitroglycerin
- FentaNYL
- MORPHine
- DimenhyDRINATE
- Atropine
- Enoxaparin
- Tenecteplase
- Clopidogrel
References
- 2023-09-10: updated consent script